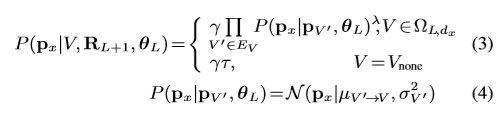引言
论文链接为:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1708.01785.pdf
论文内容主要是如何提取和理解CNN的特征处理。
名词解释
feature map: 卷积层的输出。其中我们知道每个过滤器所产生的输出是feature map的一个通道。有所疑惑的话可以看这里。explanatory graph: 论文中所要构建的解释图模型,这里简称为EG。part pattern: EG中node所表示的内容,也就是过滤器中所包含的关于图片的特征。比如马的face pattern或neck pattern。
Explanatory Graph
它有如下的特点:
- EG的每一层都与CNN的每一层卷积层相对应。
- EG的每一层的node数量等同于该卷积层中所有过滤器所包含的
part pattern。 - 自顶向下构建。
- 无监督学习。
问题:一个过滤器的feature map可能会被图像中不同位置的部分所激活
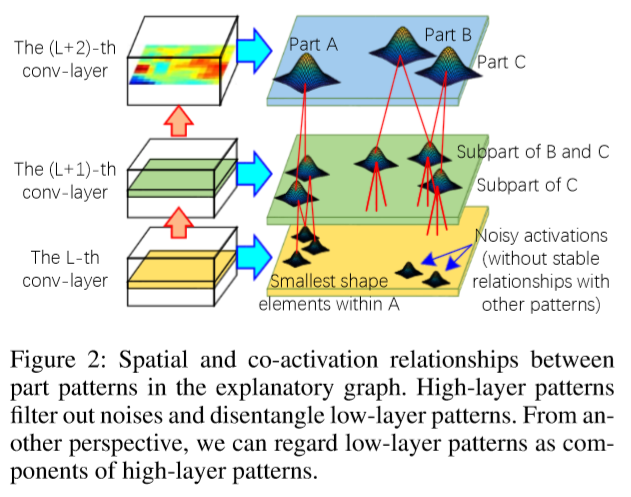
论文中的假设是如果一些peaks是由图像的相同部分造成的就称这些peaks为part patterns。否则,可能只是背景噪声所造成的。所以目标就是区分造成peaks的原因。所以说通过这种概念来建立起层级之间的联系。具体可以看这段话:
Our task is to discover activation peaks of part patterns out of noisy peaks from a filter’s feature map. We assume that if a peak corresponds to an object part, then some patterns of other filters must be activated in similar map positions; vice versa. These patterns represent sub-regions of the same part and keep certain spatial relationships. Thus, in the explanatory graph, we connect each pattern in a low conv-layer to some patterns in the neighboring upper conv-layer. We mine part patterns layer by layer. Given patterns mined from the upper conv-layer, we select activation peaks, which keep stable spatial relationships with specific upper-layer patterns among different images, as part patterns in the current conv layer. As shown in Fig. 2, patterns in high conv-layers usually represent large-scale object parts. Whereas, patterns in low conv-layers mainly describes relatively simple shapes, which are less distinguishable in semantics. We use high layer patterns to filter out noises and disentangle low-layer patterns. From another perspective, we can regard low-layer patterns as components of high-layer patterns.
建模
- Notations:
- Training Samples: $\bf{I}$
- EG: $G$
- We disentangles the $d$-th filter of the $L$-th conv-layer into $N_{L, d}$ different part patterns, which are modeled by as a set of $N_{L, d}$ nodes in the $L$-th layer of $G$, denoted by $\Omega_{L}$. $\Omega_{L, d}\subset\Omega_{L}$ denotes the node set for $d$-th filter.
- Parameters of these nodes in the $L$-th layer are given as $\theta_{L}$, which mainly encode spatial relationships between these nodes and the nodes in the $(L + 1)$-th layer.
- Given a training image $I\in\bf{I}$, the CNN generates a feature map of the $L$-th conv-layer, denoted by $X_L^I$. Then, for each node $V\in\Omega_{L, d}$, we can use the explanatory graph to infer whether $V $’s part pattern appears on the $d$-th channel of $X_L^I$, as well as the position of the part pattern (if the pattern appears). We use $R_L^I$ to represent position inference results for all nodes in the $L$-th layer.
- Objective function:
- Given inference results for the $(L+1)$-th layer ${{R_L^I}}_{I\in\bf{I}}$, we expect that all patterns to simultaneously
- be well fit to $X_L^I$
- keep consistent spatial relationships with upper-layer patterns $R_{L+1}^I$ among different images. The objective of learning for the $L$-th layer is given as $I.e.$ we learn node parameters $\theta_{L}$ that best fit feature maps of training images.
- Given inference results for the $(L+1)$-th layer ${{R_L^I}}_{I\in\bf{I}}$, we expect that all patterns to simultaneously
- 细化:
- 按我的理解,接下来作者通过假设概率分布进一步细化上述的目标函数。主要使用了Expectation-Maximization(EM) algorithm,应该类似于最大似然估计。这也就是作者在
Introduction中所说的:In this study, we propose a simple yet effective method to automatically discover object parts from a filter’s feature maps without ground-truth part annotations.
- 我还看到作者假设EG两层之间的nodes, $V$ and $V’$ follows a Gaussian distribution in Eqn.4, 其中最终的推导式如下:
- 细节部分我还是能力有限,所以就不介绍了。有兴趣的还是看原文比较好。
- 按我的理解,接下来作者通过假设概率分布进一步细化上述的目标函数。主要使用了Expectation-Maximization(EM) algorithm,应该类似于最大似然估计。这也就是作者在
实验
实验部分有个细节,即EG的层数和结点数都是人为设定的:
We selected the ninth, tenth, twelfth, and thirteenth conv-layers of the VGG-16 as four valid conv-layers, and accordingly built a four-layer graph. We extracted $N_{L, d}$ patterns from the $d$-th filter of the $L$-th layer. We set $N_{L=1or2,d}=40$ and $N_{L=3or4,d}=20$.
- pattern visualization: 分为3个小点
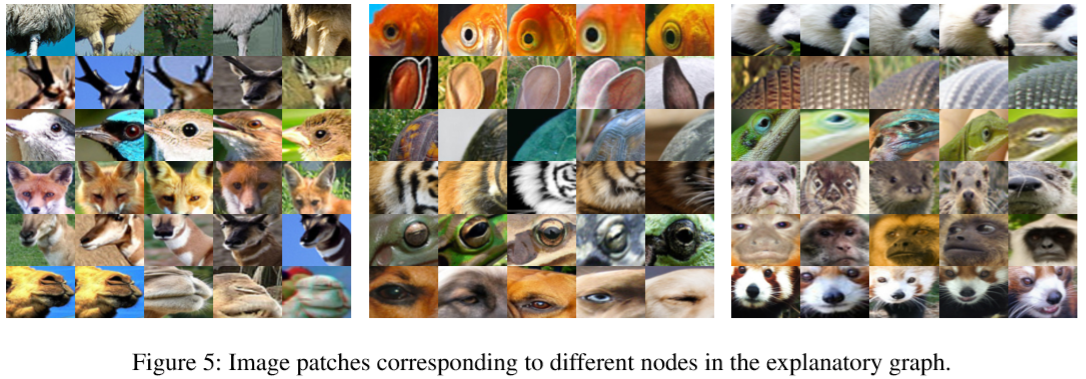
- Top-ranked patches: 这个就是截取图像中具有
highest inference scores的$70px\cdot70px$的图像块进行展示。
- Heat maps of patterns: 顾名思义,热力图。就是一张灰度图,像素值大小与激活值大小成正比。
- Pattern-based image synthesis: 整体的流程应该是保留得分最高的10%的
pattern。再将这些pattern还原成图像和原图进行比较,发现CNN识别基本上都忽略了背景,主要关注的都是前景物体部分。
- Top-ranked patches: 这个就是截取图像中具有
- semantic interpretability of patterns:
- In this experiment, we tested whether each pattern in an explanatory graph consistently represented the same object region among different images.
- Part interpretability of patterns: 通过以下两点可以看到本质上这也是很模糊的解释
- For the pattern of a given node V , we used people to
manuallyevaluate the pattern’s interpretability. - We back-propagated the center of the receptive field of each neural activation to the image plane and
simply used a fixed radiusto draw the image region corresponding to each neural activation. Fig.8 compares the image region corresponding to each node in the explanatory graph and image regions corresponding to feature maps of each filter.
- For the pattern of a given node V , we used people to
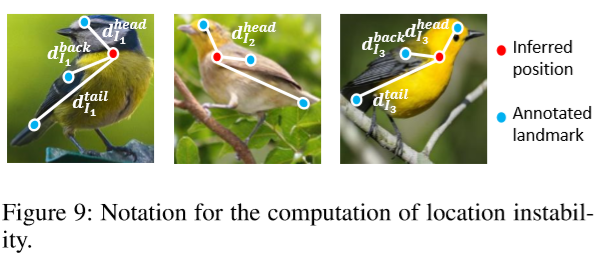
- Location instability of inference positions: 作者想验证是否一个
pattern会被不同图像的相同部分所激活。如果是这样的话,the distance between the pattern’s inference position and a ground-truth landmark of the object part should not change a lot among various images. - 作者通过计算Fig.9中红点和蓝点间的距离来确定不稳定性。
- multi-shot part localization: 主要是验证EG对于不同CNN的可转移性,看的也不是很明白。
小结
目前关于CNN或是DNN的可解释性的工作应该可以说是还在起步阶段,可以看到虽然作者设计的EG和无监督学习方式已经比较巧妙了,但是还是需要人为的一些设定和干预。